Which Best Describes Absorption in the Small Intestine
Linked to the process of absorption eg. The villi and microvilli increase the surface area of absorption.
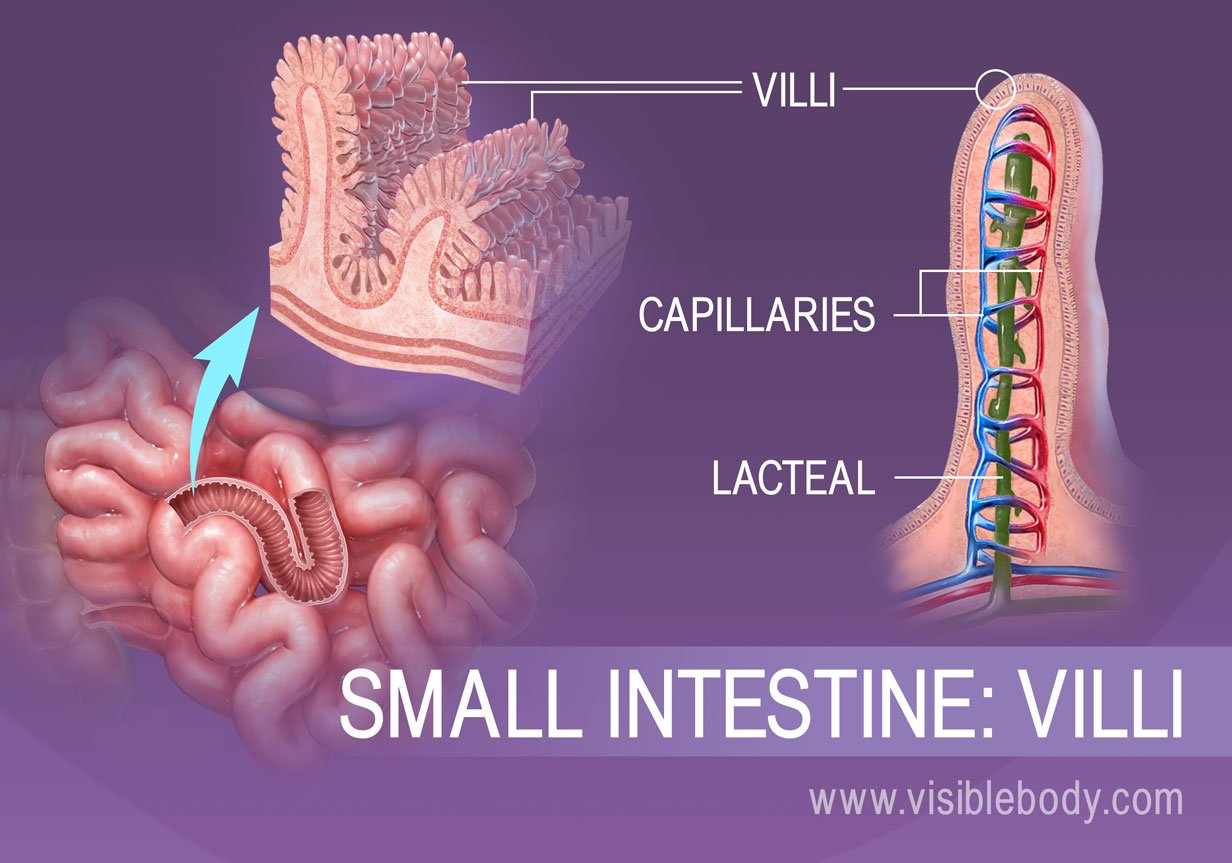
Absorption And Elimination Digestive Anatomy
Small intestine provides a huge surface area packed into a smaller space.

. The small intestine is mainly responsible for the absorption process. This organelle inside the human cell also has its own double-layered membrane. TF The circular folds of the small intestine enhance absorption by causing the chyme to spiral rather than to move in a straight line as it.
The small intestine measures approximately 6 m in length and 2530 cm in diameter. Blood transports nutrients from the small intestine to other body tissues. 2 What is a synanthropic arthropod.
From the enterocyte linoleic acid glucose and amino acids enter the bloodstream while vitamin A and vitamin E pass into the lymphatic system. Longest component of the GI tract. Describe the mechanism for small peptide absorptiondi- and tri-peptide absorption and describe.
The primary function of the small intestine is to break down. Absorption of Monosaccharides Amino Acids Dipeptides Tripeptides Lipids Electrolytes Vitamins and Water Glucose amino acids fats and vitamins are absorbed in the small intestine via the action of hormones and electrolytes. Question 26 1 pts Which statement best describes the absorption of nutrients.
First week only 499. The average adult usually ingests 1-2 L of water each day but the fluid load to the small intestine is 9 to 10 L 8 to 9 L being added by secretions of the GI system. The small intestine is the part of the digestive system which is very long in its length but small in diameter.
The thin surface layer. From the cells of the small intestine amino acids and glucose pass into the bloodstream while long chain fatty acids pass into the lymphatic system. Which of these best describes a lacteal.
The small intestine begins after the stomach and the main parts of the intestine are duodenum jejunum and ileum. 1 Active transport is a process requiring energy ATP and a nutrient carrier to move an essential nutrient against a. The small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract between the stomach and the large intestine where much of the digestion of food takes place.
Small intestine Site of iron calcium folate absorption Preferentially in the duodenum Site of B12 and bile acids Preferentially in the ileum Mucosal digestion Digestion occurring at the mucosal surface. An image of a simplified structure of the villus. It is referred to as the small intestine because its lumen opening is smaller in diameter at approximately 25 centimeters or 098 inches than the large intestine colon.
Nearly all of the nutrients you take in through your mouth are absorbed through the wall of the small intestine. Much of digestion and absorption of food takes place in the small intestine. The interior surface of the small intestine shrinks into folds which triples the surface area for absorption.
Nephrons filter the blood in the small intestine before the nutrients are transported to other tissues. Most absorption of water and electrolytes occurs in the small intestine with some water absorbed in the colon as well. The blood in the small intestine is filtered through the glomerulus before blood vessels transport the nutrients to other tissues.
Absorption occurs by a saturable active transport process at lower levels of dietary copper and by passive diffusion at high levels of dietary copper. B Glands called Peyers patches are responsible for acid secretion. C The vagus nerve inhibits acid secretion after a meal has been consumed.
The primary function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutrients and minerals found in food. Such folds are spread over with villi finger-like projections which expand the absorptive area to 10 more folds. A Acid secretion occurs in response to secretion of the hormone carbonic anhydrase.
The Small intestine is a coiled hollow tube that extends from the stomach to the large intestine. Brush border enzymes Intracellular digestion Digestion occurring within the epithelial cell. Learning Objectives Describe the process of absorption of nutrients in the small intestine Key Takeaways Key Points.
The primary function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutrients and minerals which are found in foodSmall intestine is the longest part of alimentary canal. The small intestine is the main site for the digestion of chyme and absorption of the nutrients from the digested material. The colon measures approximately 15 m in length with a diameter of 675 cm.
The small intestine has a very smooth flat inner lining to minimize nutrient absorption. It extends from the pylorus of the stomach to the junction between cecum and ileum. D Pepsinogen and gastric lipase are two enzymes secreted into the lumen of the stomach.
Copper is absorbed in the proximal small intestine and stomach. Food is broken down into individual nutrients and molecules. In fact it is the longest portion of the digestive system approximately 20 to 25 feet in length.
Virtually all nutrients from the diet are absorbed into blood across the mucosa of the small intestine. Solution for Describe the cellular mechanisms of Ca absorption in the small intestine. Substances are taken up from the GI tract and enter the bloodstream or the lymph.
What is the best synapomorphy for Phylum Mollusca. Best Answer Copy ABSORPTION is accomplished by one of four mechanisms. The surface area of the small intestine is significantly enhanced by the presence of villi and microvilli which increase the intestinal surface area by 30600 fold respectively.
Which statement best describes the absorption of nutrients. From the cells of the small intestine glucose and vitamin C enter the bloodstream while EPA and vitamin A enter the lymphatic system. In addition the intestine absorbs water and electrolytes thus playing a critical role in maintenance of body water and acid-base balance.
Hence the small intestine has villi and not the stomach. All carbohydrates are absorbed as these. Microvilli are hairs that aid in absorption of nutrients.
A a projection of the small intestine wall designed to increase surface area B special capillaries in the villi designed for absorbing food effectively. Start your trial now. Any undigested or unabsorbed material left in the small intestine is passed here.
Its probably fair to say that the single most important process that takes place in the small gut to make such absorption possible is. Which of the following statements regarding mitochondria is false. Which Definition best describes absorption.
The stomach on the other hand is an organ that primarily stores food temporarily along with the digesting proteins. Simple diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis active transport. The Small Intestine.
Brief About The Absorptive Structures Of The Small Intestine. Four methods of absorption in the small intestine.
Which Carries Digested Food From The Small Intestine To The Bloodstream Quora

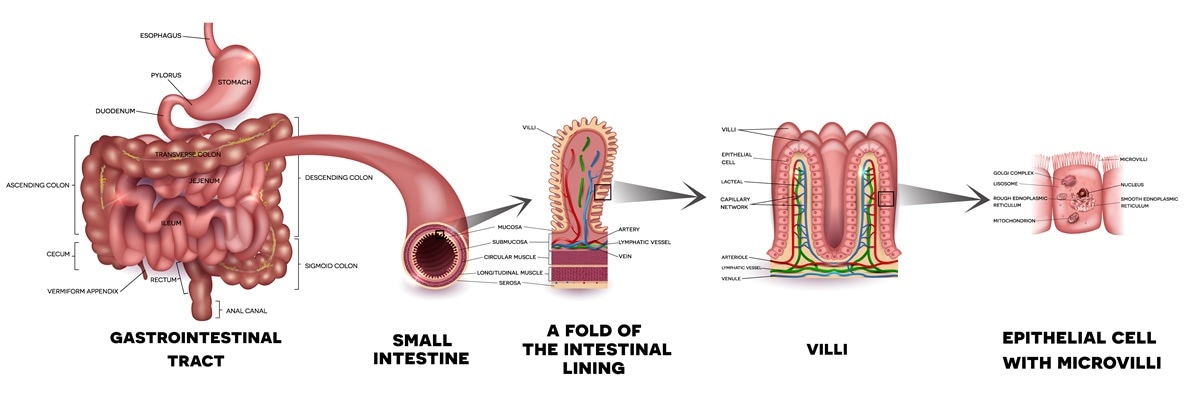
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Which Best Describes Absorption in the Small Intestine"
Posting Komentar